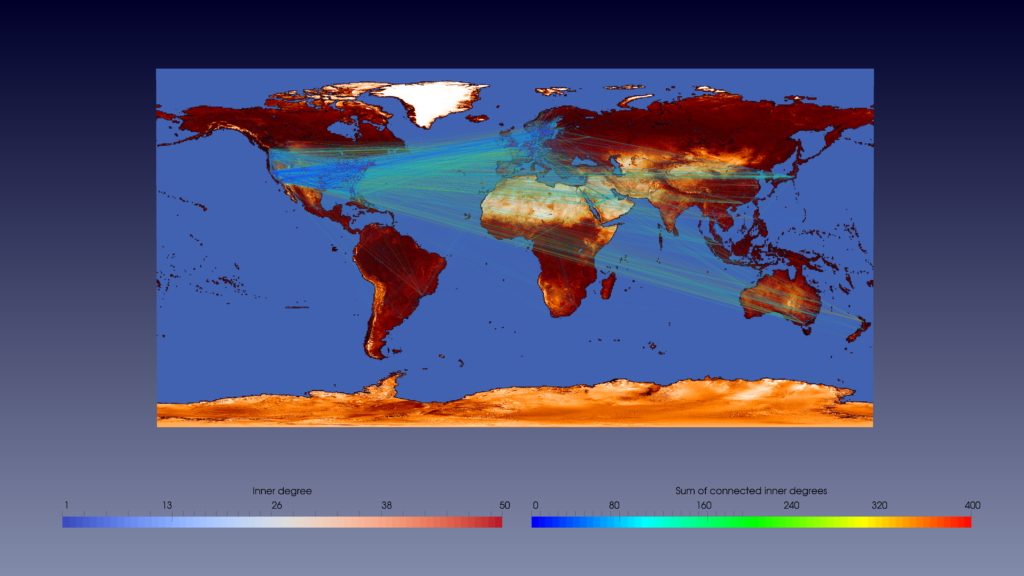
The globalisation of humanity’s social and industrial activities, as observed over the past decades, has caused a growing need to address the global risks and opportunities involved. Some of these prominent challenges include:
- The global health risks – from diabetes to pandemics – involved in the spread of unhealthy social habits as well as the opportunity to achieve major global health improvements through healthy behaviour.
- The global diffusion of green growth initiatives, including policy initiatives, business strategies and lifestyle changes for successful as well as inefficient pathways.
- The challenges of global urbanisation, with special focus on the impact of infrastructure decisions regarding indicators like congestion, real estate prices and greenhouse gas emissions.
Approaches that address the above-mentioned challenges are investigated by a newly-emerging research area: Global Systems Science (GSS). However, with these transdisciplinary problems the demand for compute performance due to data and time constraints increases drastically so that the assistance of High Performance Computing (HPC) is mandatory. Therefore, the CoeGSS Project brought together both communities and developed an environment for successful collaboration between the stakeholders dealing with Global Challenges on the one hand and the High Performance Computing institutions that provide the mandatory capabilities to address those complex challenges on the other.
So far, the use of HPC in GSS studies for processing, simulating, analysing, and visualizing large and complex data has been very limited due to a lack of tailored HPC-enabled tools and technologies. Within CoeGSS, those issues have been addressed by developing models, simulations, but also the technology and tools to interpret the output data efficiently. Typical GSS applications are data-bound, whereas traditional HPC tools and libraries are optimized to solve computationally intensive problems so that their applicability is limited for this emerging domain. Consequently, one major goal of the CoeGSS project was to establish a robust technology base in order to execute network, and in particular memory intensive applications in a scalable manner.
Nevertheless, the main difference between typical HPC and GSS applications lies in the data sources and outputs as well as the used algorithms. Whereas lots of traditional high-performance application codes, like those of computational fluid dynamics, require massive parallelism and high computational power, GSS applications demand additional capabilities, for instance huge and varying data or in a generic manner, data-centric computation. Thus, looking for a trade-off between the data-centric programming models of the Cloud infrastructures and the highly efficient and scalable HPC technologies has been one of the key challenges for the CoeGSS project.