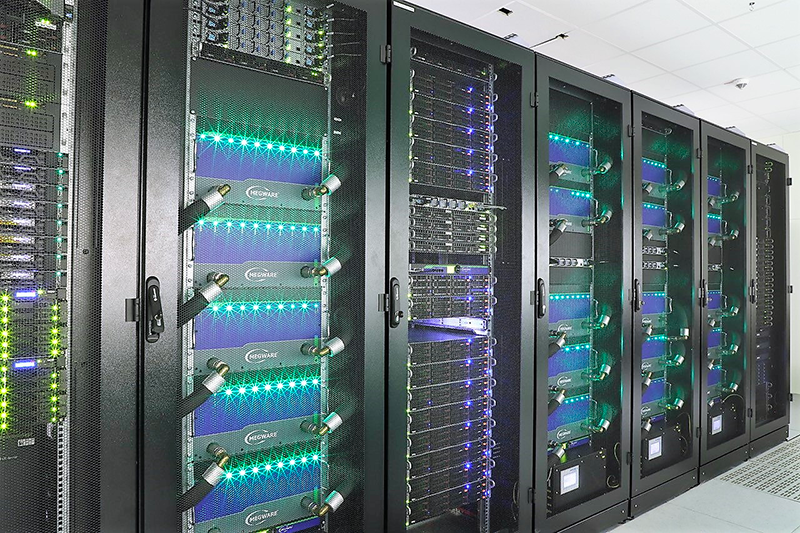
There is more than one way to build a super-computer, and meeting the diverse demands of modern applications, which increasingly combine data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) with simulation, requires a flexible system architecture. Since 2011, the DEEP series of projects (DEEP, DEEP-ER, DEEP-EST) has pioneered an innovative concept known as the Modular Supercomputer Architecture (MSA), whereby multiple modules are coupled like building blocks. Each module is tailored to the needs of a specific class of applications, and all modules together behave as a single machine.
Connected by a high-speed, federated net-work and programmed in a uniform system software and programming environment, the supercomputer allows an application to be distributed over several hardware modules, running each code component on the one which best suits its particular needs. Specifically, DEEP-EST, finished in March 2021, has built a prototype with three modules: a general-purpose Cluster Module (CM) for low or medium scalable codes, the highly scalable Extreme Booster Module (ESB) comprising a cluster of accelerators, and a Data Analytics Module (DAM), which were tested with six applications combining high-performance computing (HPC) with high-performance data analytics (HPDA) and machine learning (ML).
The DEEP approach is part of the trend to-wards using accelerators to improve performance and overall energy efficiency – but with a twist. Traditionally, heterogeneity is done within the node, combining a central processing unit (CPU) with one or more accelerators. In DEEP-EST the resources were segregated and pooled into compute modules, as this enables to flexibly adapt the system to very diverse application requirements. In addition to usability and flexibility, the sustained performance made possible by following this approach aims to reach exascale levels.
One important aspect that makes the DEEP architecture stand out is the co-design approach, which is a key component of the project. In DEEP-EST, six ambitious HPC/HPDA applications were used to define and evaluate the hardware and software technologies developed. Careful analysis of the application codes allowed a fuller understanding of their requirements, which informed the proto-type’s design and configuration.
In addition to traditional compute-intensive HPC applications, the DEEP-EST DAM includes leading-edge memory and storage technology tailored to the needs of data-intensive work-loads, which occur in data analytics and ML.
Through the DEEP projects, researchers have shown that combining resources in compute modules efficiently serves applications from multi-physics simulations to simulations integrating HPC with HPDA, to complex heterogeneous workflows such as those in artificial intelligence applications.
The next step in the series of DEEP projects is made with DEEP-SEA – Software for Exascale Architectures.